Describe the Use of Restriction Enzymes in Genetic Engineering
They are used in RFLP techniques to cut the DNA into smaller fragments to study the fragment length differences among the individuals. Restriction enzymes are used to cut the chromosomes into small segments which are then cut into even smaller pieces until the sought-after gene is found.
Genetic Engineering Restriction Enzymes And Plasmids Recombinant Dna Technology Biofoods
An extremely important use of.

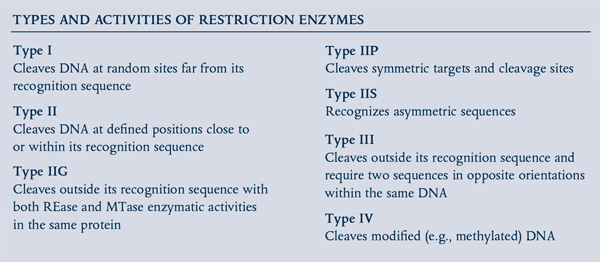
. Blunt end cutters Type II restriction enzymes of this class cut the DNA strands at same points on both the strands of DNA within the recognition sequence. They are specific endonuclease enzymes in the cells which first recognize the specific sequence called restriction sites within the DNA strand and cleave the phosphodiester backbone of the DNA at specific sites. Restriction enzymes are also frequently used to verify the identity of a specific DNA fragment based on the known restriction enzyme sites sequence that it contains.
DNA ligase is a DNA-joining enzyme. Refer to June 2011 paper Scientists used restriction mapping to investigate some aspects of the base sequence of an unknown piece of DNA. Use of Restriction Endonuclease Enzymes in Genetic Engineering.
However the first restriction endonuclease enzyme to be isolated and studied was E. Restriction enzymes are used in genetic engineering for gene manipulation. A bacterium uses a restriction enzyme to defend against bacterial viruses called bacteriophages or phages.
Restriction endonuclease enzymes play an important role in cutting. Using restriction endonuclease restriction enzyme reverse transcriptase to get DNA and produce sticky ends. The main steps of genetic engineering.
Restriction Enzyme A restriction enzyme is an enzyme isolated from bacteria that cuts DNA molecules at specific sequences. Many restriction enzymes make staggered cuts producing ends with single-stranded DNA overhangs. They cut the base pairs within the molecule so they are named as an endonuclease.
Use of restriction enzyme in genetic engineering Restriction enzymes cut the DNA at some specific sites they may be endonuclease or exonuclease. Restriction enzymes are DNA-cutting enzymes. Restriction enzymes can be used to map DNA fragments or genomes.
That is why prokaryotic organisms like E. For this reason they are indispensible tools of recombinant DNA technology genetic engineering. It cuts DNA base pairs at specific sites.
Mapping means determining the order of the restriction enzyme sites in the genome. Restriction enzymes also known as restriction endonucleases REases are the basic tools of molecular biology. A vector is needed to get the gene into the host cell.
View the full answer. Scientists can use restriction enzymes to cut a single gene from a larger piece of. Applications of Restriction Enzymes.
These attack bacteria and try to infect them by inserting their DNA in the cells of the bacteria. In gene cloning experiments DNA molecules have to be cut in a very precise and reproducible manner. Recognise foreign genetic code prokaryotic organisms use restriction enzymes to identify and cut foreign DNA.
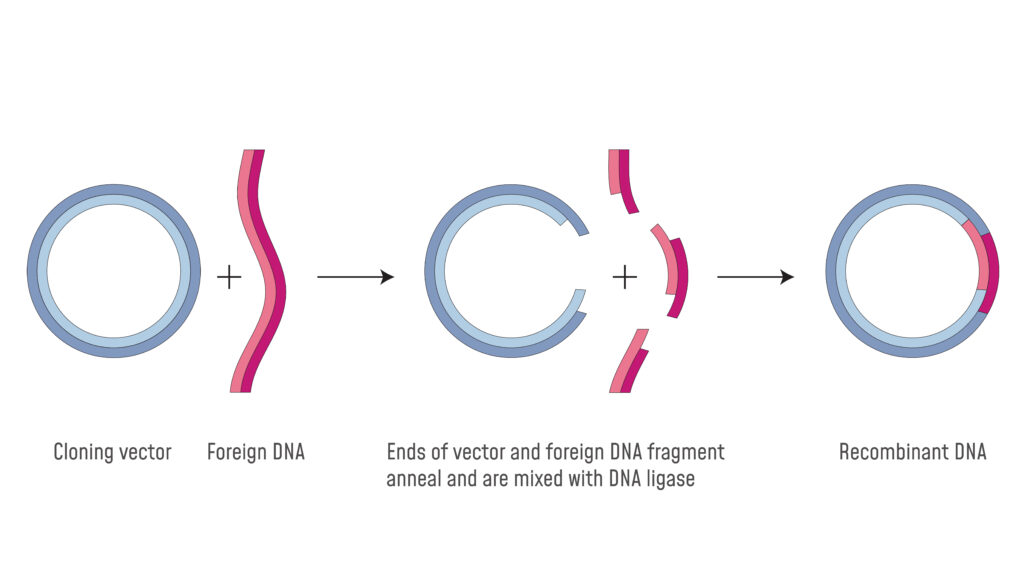
Use ligase to join wanted gene to plasmid. Physical DNA mapping Since the first experiments by Danna and Nathans 1971 the major use of restriction enzymes was aimed at locating their cutting sites on selected DNA molecules. Restriction enzymes can be isolated from bacterial cells and used in the laboratory to manipulate fragments of DNA such as those that contain genes.
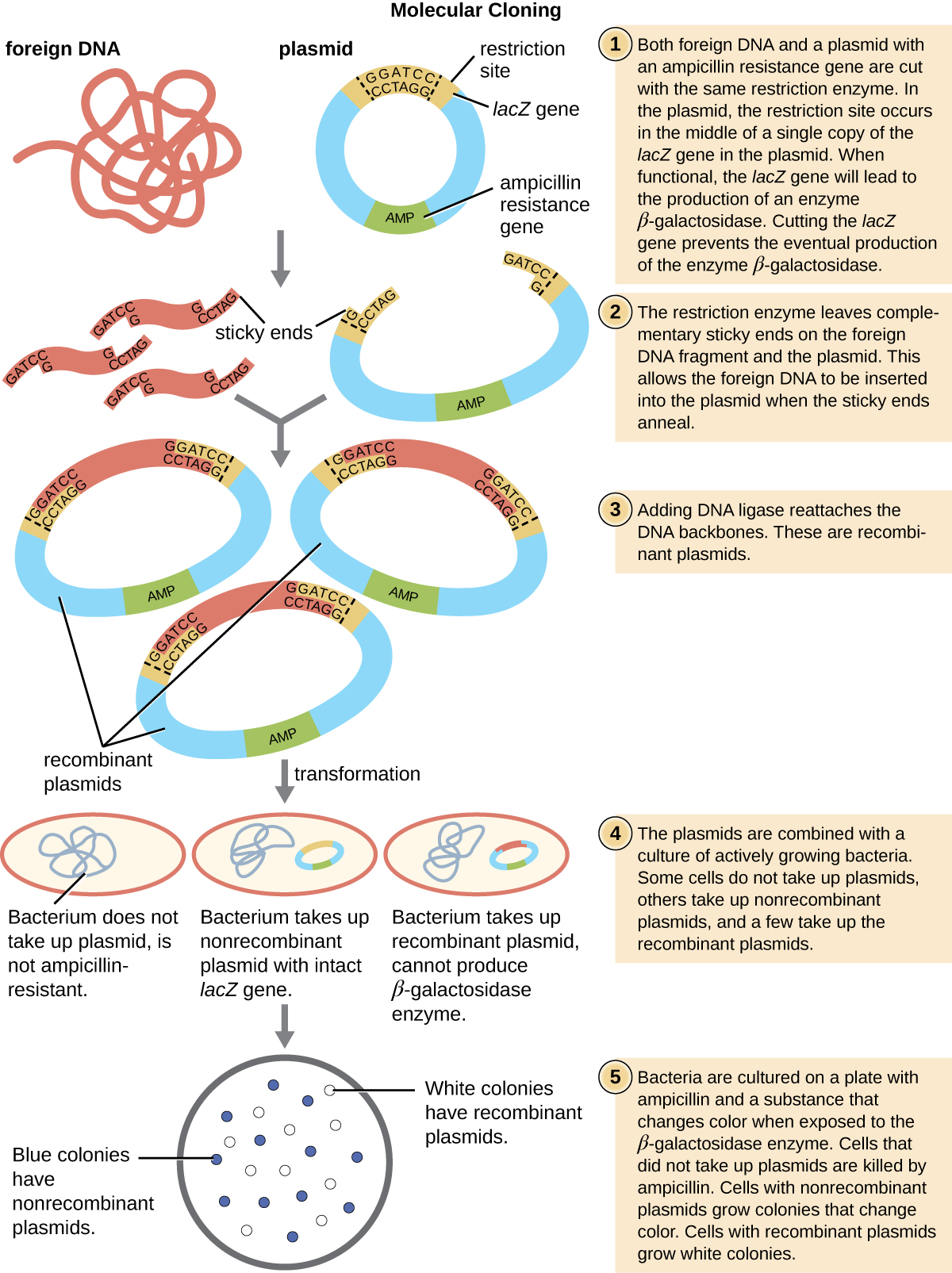
During cloning a gene is inserted into a plasmid. Each enzyme recognizes one or a few target sequences and cuts DNA at or near those sequences. Add plasmid to bacteria to grow coloniesthen replica plate onto medium where the marker gene is expressed.
Also include marker gene eg. You can think of restriction enzymes as molecular scissors. The ability of restriction enzymes to reproducibly cut DNA at specific sequences has led to the widespread use of these tools in many molecular genetics techniques.
The term restriction endonuclease was coined by Lederberg and Meselson 1964 to describe the nuclease enzymes that destroy restrict any foreign DNA entering the host cell. They cut the DNA at a specific sequence. Type II Restriction Enzymes - Cohesive End Cutters.
The DNA strands generated are completely base paired. This piece of DNA was 3 000 base pairs bp long. Coli bacteria use systems based on the ability to recognise virus DNA code.
Such fragments are called as blunt ended or flush ended fragments. In both cases the cut-and-paste techniques developed by genetic engineering are indispensable. Basic use of restriction enzymes.
They form part of the restriction-modification systems which usually consist of an. Bacteria use restriction enzymes to protect themselves from a dangerous virus called a bacteriophage which translates to bacteria eater in literal terms. The isolation of these enzymes was critical to the development of recombinant DNA rDNA technology and genetic engineering.
The scientists took plasmids that had one restriction site for the enzyme Kpn1 and one restriction site for the enzyme BamH1. However some produce blunt ends. 3000 restriction enzyme has been discovered till now.
A restriction enzyme is used as an important tool for genetic engineering. Class I III and IV restriction enzymes is often ATP-depen-dent reviewed in Roberts et al. Restriction endonucleases also called as molecular scissors are a class of nuclease enzymes which cut the DNA strand at precise locations.
Restriction enzymes are used to isolate the required gene from the chromosome. To cut DNA all restriction enzymes make two incisions once through each sugar-phosphate backbone ie each strand of. Restriction enzymes can be used to map DNA fragments or the entire genome thus determining the specific order of the restriction enzyme sites in the genome.
A restriction enzyme or restriction endonuclease is an enzyme that cuts DNA at or near specific recognition nucleotide sequences known as restriction sites. Restriction enzymes cut the plasmid producing single-stranded overhangs. They are enzymes that cleave double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acids DNAs in a sequence-specific manner and are ubiquitously present among prokaryotic organisms.
Viruses are smaller than cells and they inject their DNA inside the cell to multiply itself after this attack cell dies. This is usually a plasmid that.
Restriction Endonucleases Molecular Cloning And Beyond Neb

3 What Is Dna Ligase Labxchange

Restriction Endonucleases Molecular Cloning And Beyond Neb
Restriction Enzymes 101 Nordic Biosite

Genetic Engineering An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Restriction Enzymes An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Recombinant Dna Creating The Clone Britannica
10 1 Microbes And The Tools Of Genetic Engineering Biology Libretexts

Restriction Enzymes Micah Matthews And Hannah Perryman Ppt Download

Enzymes For Genetic Engineering Ppt Download

Restriction Endonucleases Molecular Cloning And Beyond Neb
4 4 Genetic Engineering And Biotechnology Bioninja

What Purpose Do Enzymes Serve In Genetic Engineering Quora
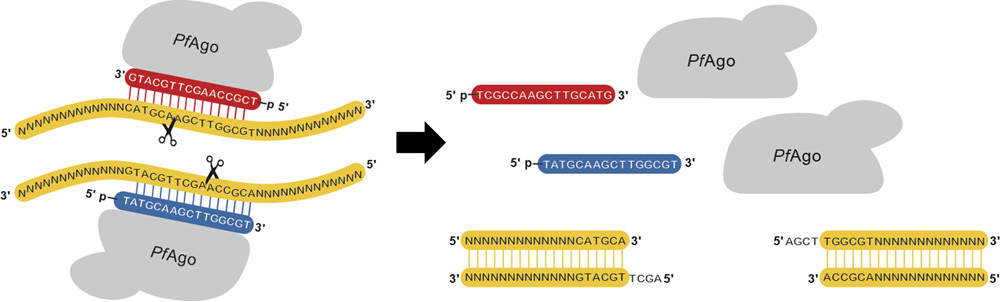
New Genetic Engineering Method Indispensable Biotechnological Tool Carl R Woese Institute For Genomic Biology

Title Genetic Techniques 1 Ppt Video Online Download

Restriction Enzymes And Molecular Cloning E Zyvec



Comments
Post a Comment